Does Metal Have Memory? Nitinol - A Nickel Titanium Alloy
25.04.2020
Varzene Metal
Nickel-Titanium alloys are intermetallic compounds where nickel and titanium elements coexist at an almost equal atomic rate. Intermetallic compounds are stronger compounds because they are composed of metals that are not alike. The presence of the compounds in the covalent bond causes them to have different properties in terms of mechanical, chemical and electrical.
The name of these alloys known today is "metals with memory". It has a very hard structure at high temperatures, but its flexibility increases as its temperature decreases. The reason for this is that the atoms in NiTi are different in hot environment and different in cold environment. At low temperatures, the shape of the atoms in the crystal structure changes when heated, while the shape can change with the force applied on them, they return to their previous positions without permanent deformation. Although a shock cooling is applied, it has the ability to permanently store this shape.
Nickel-Titanium alloys are used especially as biomaterials. Thanks to its shape memory feature and elasticity, they can be used in fixing the broken jaw bones and skull bones, living tissue prostheses, placing the vertebrae, and dental implants. However, due to its lightness and porous structure, it also reduces the risk of fracture in the bones.
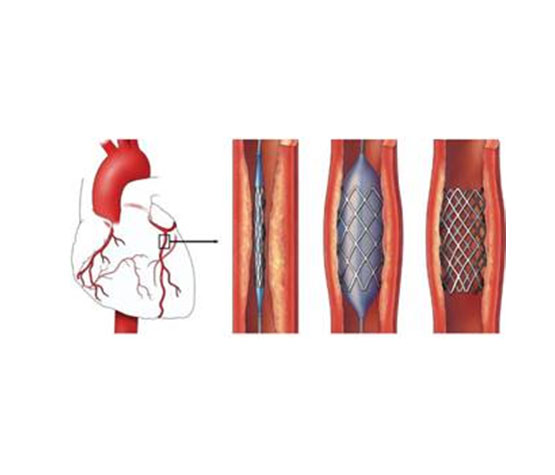
As an important innovation, the load resistance is quite good in order to make the shape memory metals, which are frequently encountered in the medical field in recent years, change the body repeatedly, is one of the materials used in the production of stents that provide opening of the occluded heart vessels. The stents produced in the form of tubular, memory-like metals in a vein-like structure are shrunken and placed in the occluded vessel in the martensitic phase. Since the temperature it changes is close to the body temperature, when its temperature increases with the effect of body temperature, it passes into the austenitic phase, expanding and opening the occluded vein. With this material, which lasts 20 years in the human body, treatment of important diseases will be provided.
References:
- Acar E, 2018. Biomedical applications of shape memory alloys
- Auricchio F, Boatti E, Conti M. 2015. SMA biomedical applications, Shape Memory Alloy Engineering, ButterworthHeinemann
- www.malzemebilimi.ne